Receding Gums: A Guide to Detection and Treatment
Receding gums are typically indicators of more significant oral health conditions that carry serious implications such as tooth decay and tooth loss.
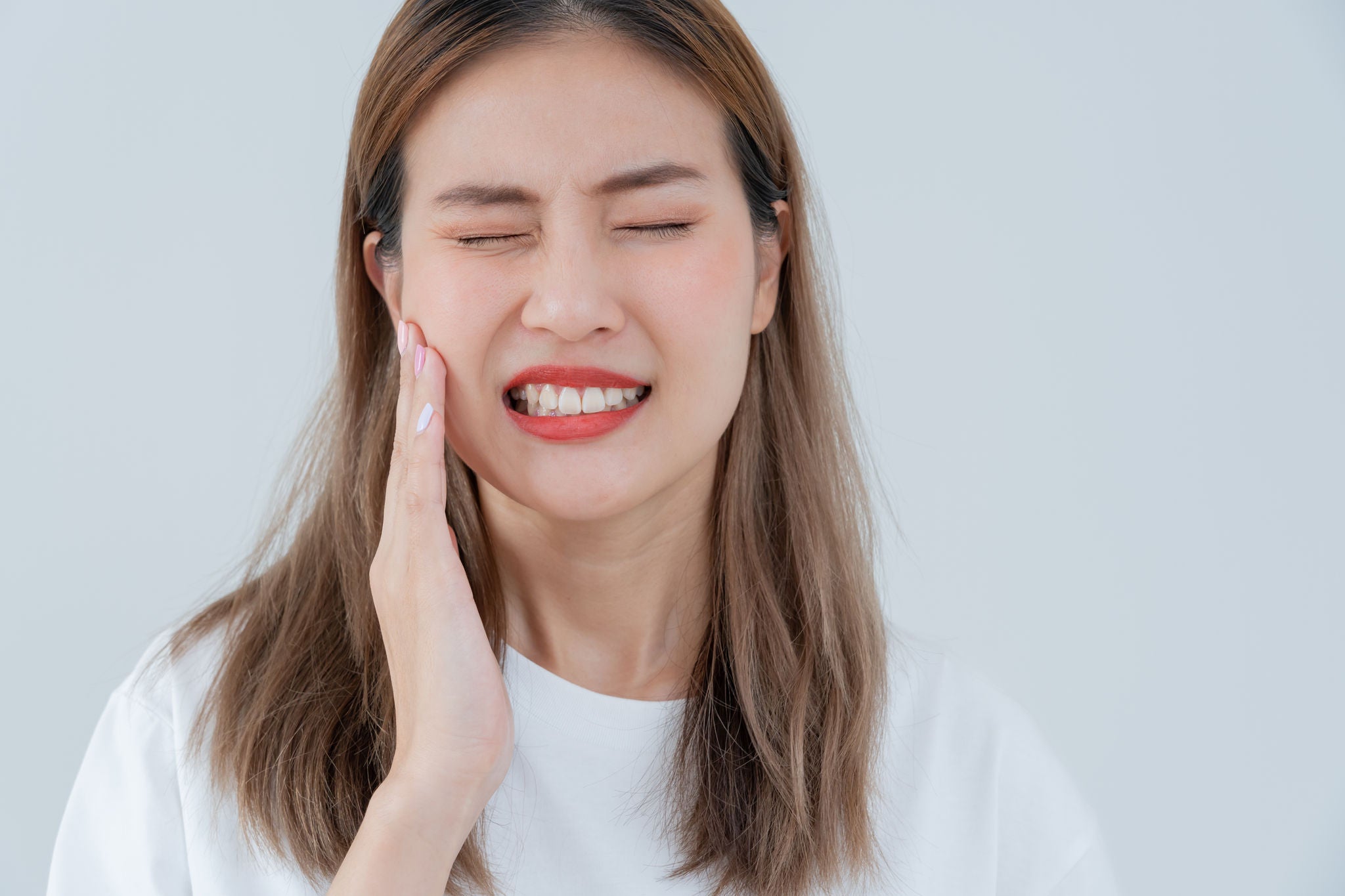

Gum tissue cannot be regrown, so once it has receded the only way to fully restore missing gum tissue, is typically through surgical intervention.
This guide will help you understand what causes receding gums, available treatments, and which habits promote healthy gums.
How to tell if your gums are receding
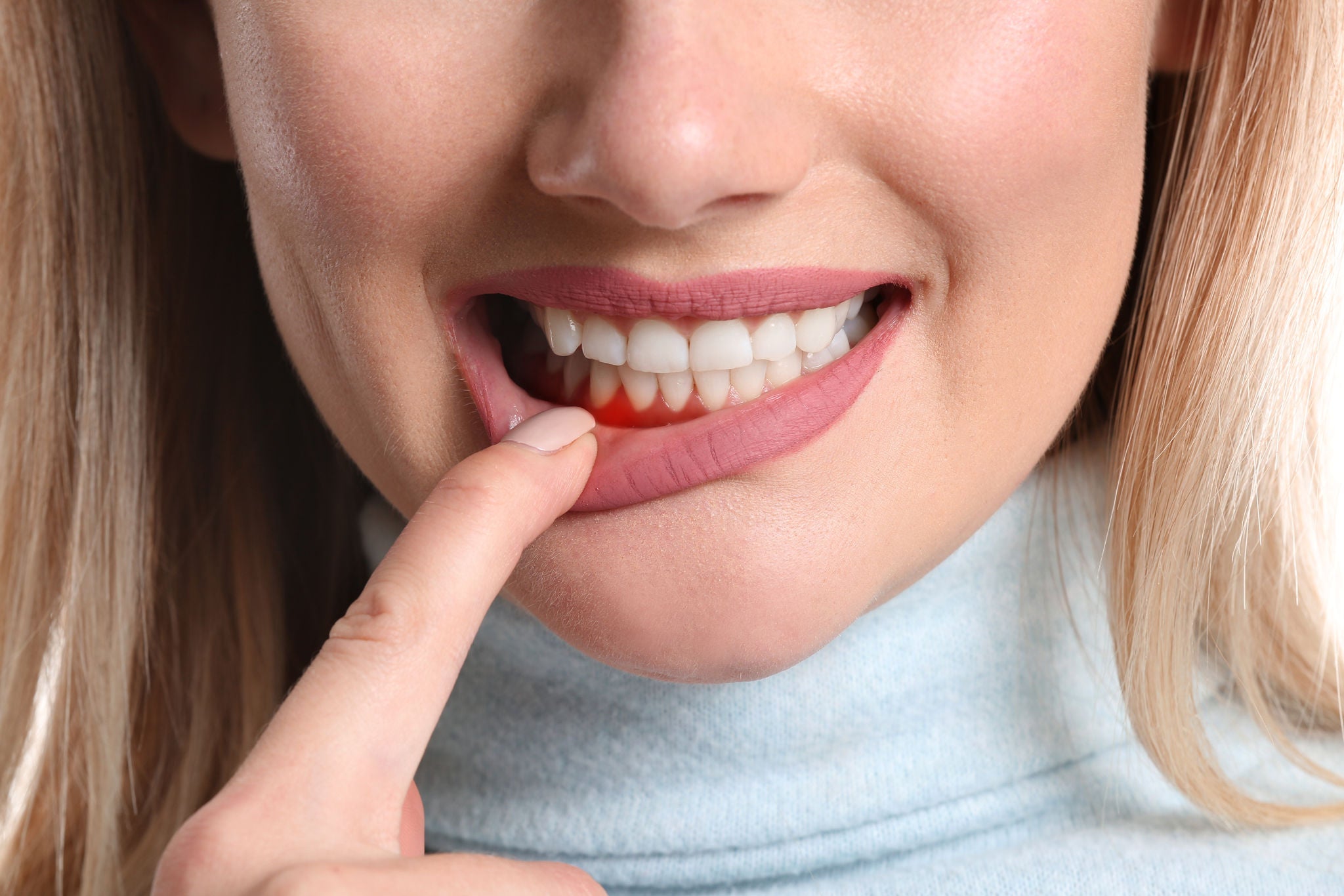
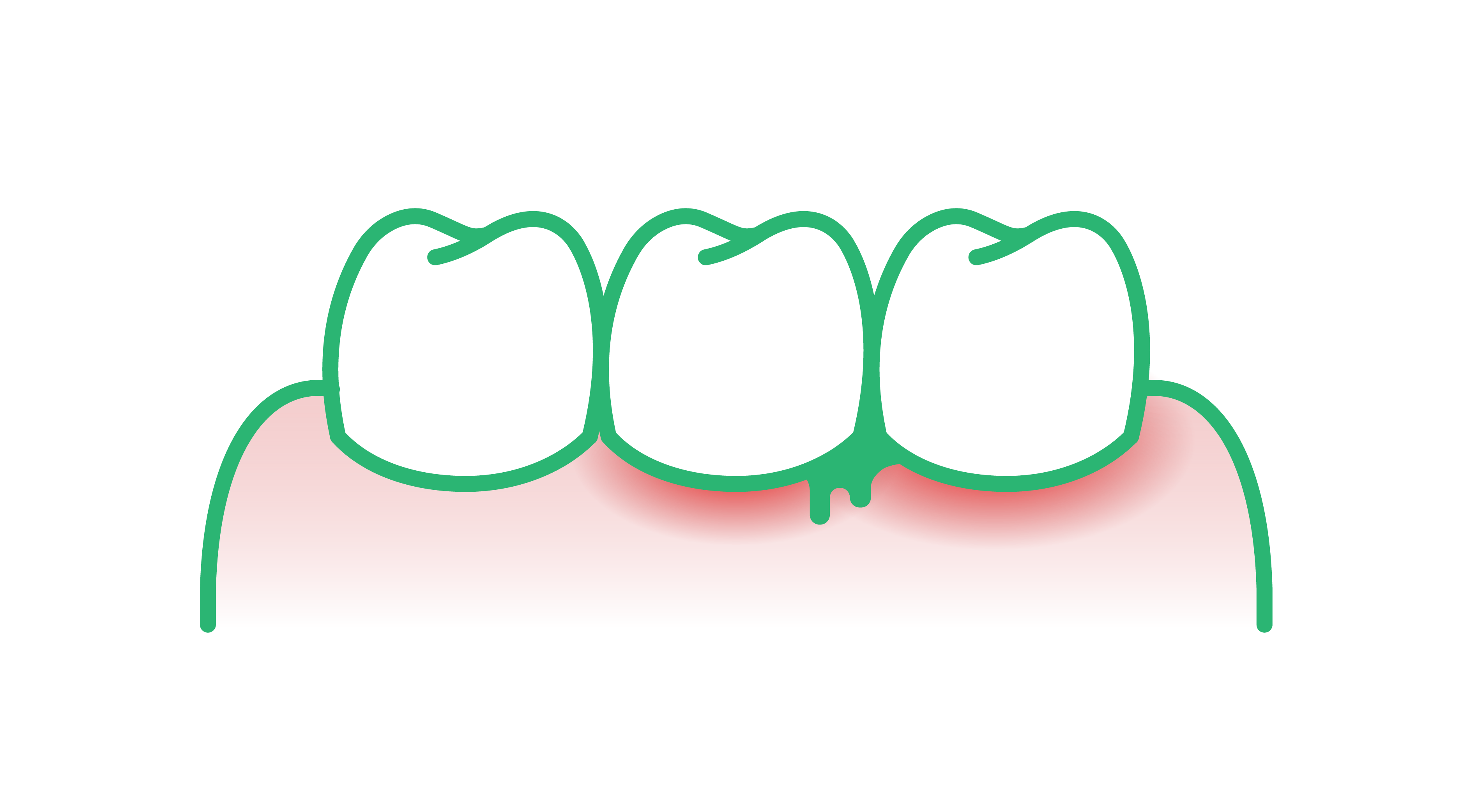
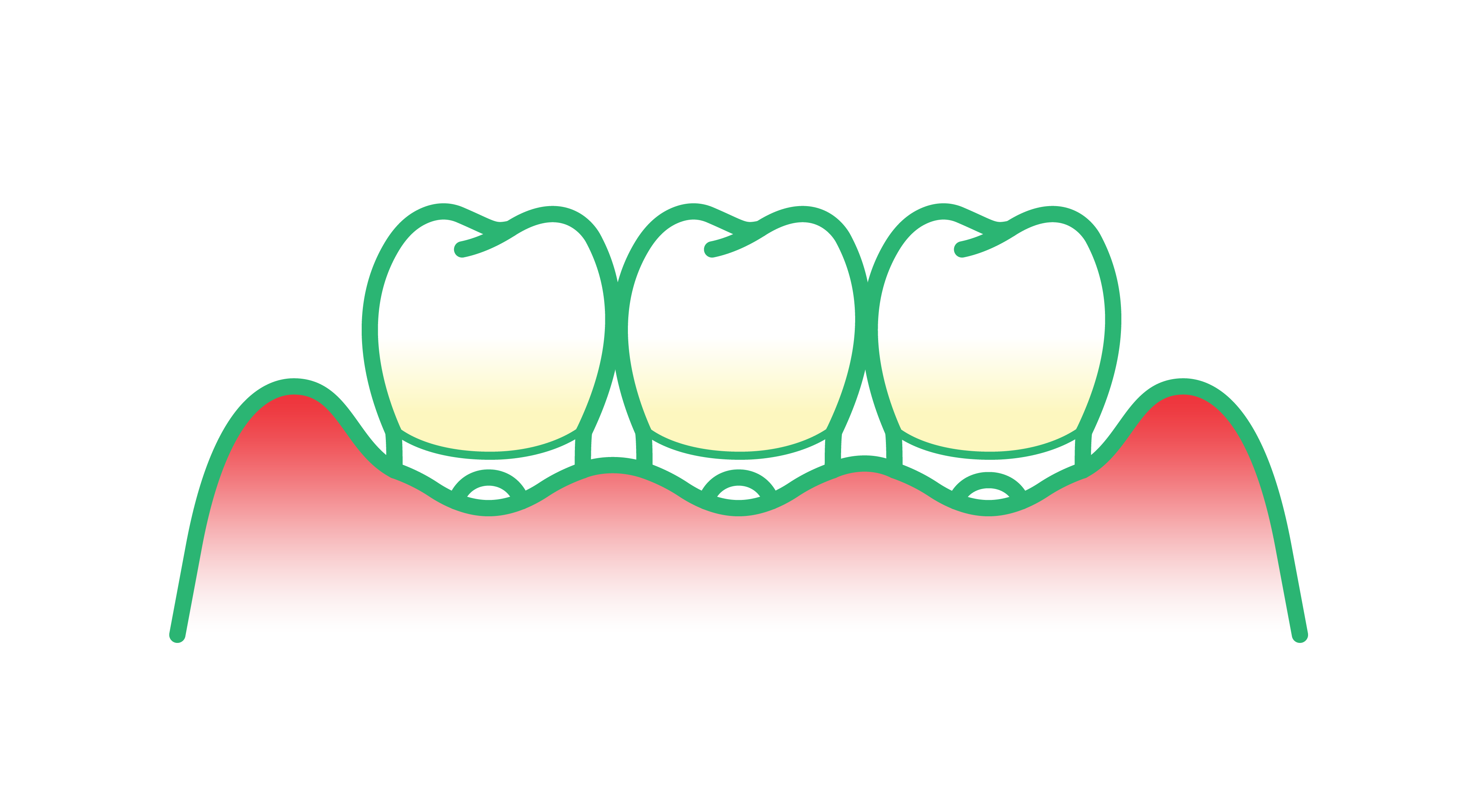
Receding gums is a condition where the gum tissue that surrounds the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing the roots of the teeth.
Common signs of receding gums
- Tooth sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures or sweet or acidic foods and drinks.
- Visible roots: Teeth that appear longer than they used to.
- Gap at the gumline: A noticeable retraction of the gumline.
- Loose teeth: Teeth that feel as if they have become loose or shifted in position.
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, it's important to see your dentist as soon as possible. Your dentist will examine your gums and teeth and may take X-rays to determine the severity of the condition.

What causes receding gums?
A number of direct and indirect factors can lead to receding gums. These are the most common causes.
Forceful brushing
Over time, brushing too aggressively can cause gum recession. This is the result of repeated, prolonged pressure that pushes gum tissue down and away from the teeth. While forceful brushing is a mechanical factor and not indicative of existing disease, damaged gum tissue and exposed teeth are more susceptible to infection.
Gum disease
What people commonly refer to as gum disease is actually a progression of disease within the gum tissue defined by two stages: gingivitis and periodontitis.
There are 4 stages of periodontitis: Initial, Moderate, Severe, and Advanced
These stages are determined by the severity, complexity, and extent of the disease based on factors such as recession of the gums, bone loss, loose teeth, and lost teeth.
With each of these stages come 3 grades (A, B, C) that define the rate of progression of the disease. These stages are based on the quantity of bone loss over the years and risk factors like smoking and diabetes.
Early detection and treatment of gum disease are crucial in preventing receding gums and damage and preserving oral health.
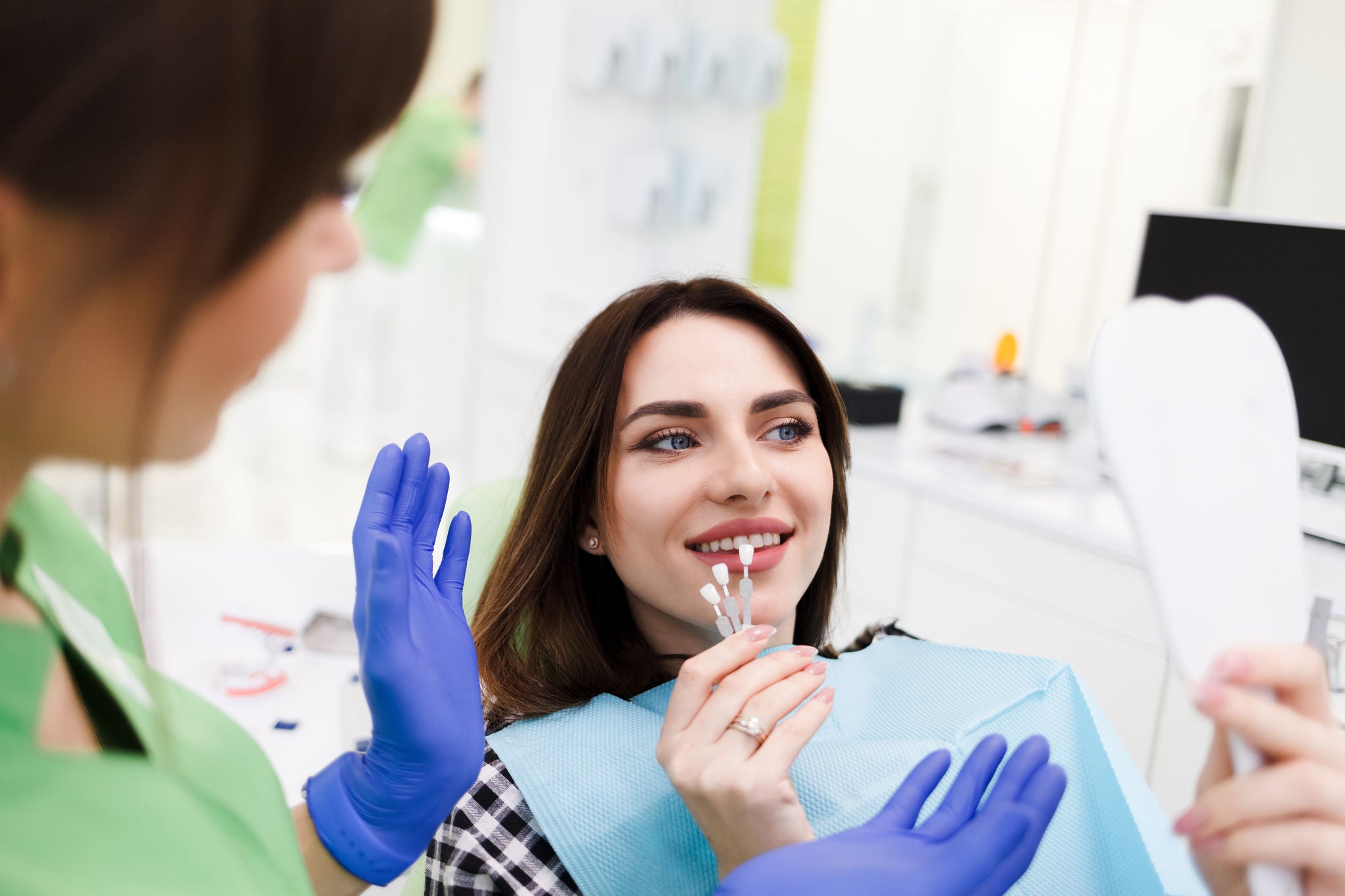
Treatment for receding gums
Depending on the cause of receding gums, there are both non-surgical and surgical treatments available.
Treatment for receding gums caused by gum diseases
Deep dental cleaning, otherwise called scaling and root planing, removes harmful plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gum line. This can help to reduce inflammation and promote gum reattachment. Deep dental cleaning is one component of a complete gum disease treatment plan.
Additional treatments within this plan include a strict oral hygiene regimen, a commitment to lifelong maintenance by the patient, and supportive periodontal therapy by professionals after initial treatment. Periodontal surgeries may be recommended.
Treatment for gum recession caused by mechanical trauma
It is essential to first address the underlying cause of gum recession to prevent further damage and maintain gum health. For example, if gingival recession was caused by a traumatic brushing technique, a more appropriate brushing technique will need to be adopted before any surgery is considered.
Gum grafting surgery is a common treatment option for gingival recession that involves the transfer of gum tissue from one part of the mouth to another. The goal of the procedure is to cover exposed tooth roots and restore the gumline to a healthy position.
How to prevent receding gums
Maintaining a good oral hygiene ritual is paramount, including interdental cleaning, twice-daily brushing, and using a mouth rinse. When brushing, it is important to use good technique and avoid brushing too forcefully.
Orthodontics can also be employed to reduce the risk of receding gums. Teeth that are too tight, tipped, or crooked can create spaces for food and bacteria to be trapped, increasing the risk of gum disease and gum recession. Orthodontics can help resolve this problem by moving teeth into proper alignment.
Regular visits to a dental professional for check-ups and professional cleaning are crucial. Early detection of gum disease can help prevent further damage to the gums and teeth. By adhering to these recommendations, individuals can effectively avoid receding gums and maintain optimal oral health.